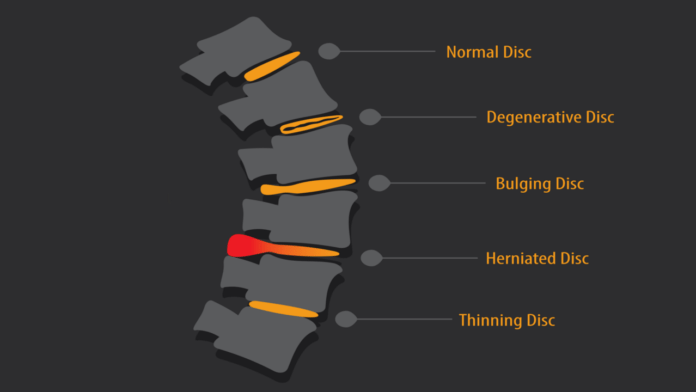
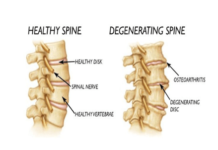
Discs of cartilage act as cushions between the vertebrae or bones in the spine. These cushions are known as intervertebral discs. When a disc is herniated, some of its soft center, the nucleus pulposus, has pushed through its tough exterior. The formal medical term for this condition is “herniated nucleus pulposus” or HNP.
A herniated nucleus pulposus has the potential to irritate nerves, thereby causing pain, numbness or weakness in a limb. A person experiencing any of these symptoms should seek medical attention immediately. However, many people with herniated discs experience no symptoms. In most cases, a slipped disc does not require surgery. Slipped disc treatment can be as simple as performing herniated disc exercises alone or with a physical therapist.
When reading about HNP, herniated disc symptoms and related topics, you’ll probably see several interchangeable terms and spellings. Herniated discs are sometimes called “slipped discs” or “ruptured discs” in common parlance. You might also read about cervical disc herniation, which relates to the vertebrae in the upper spine. Cervical disc herniation might be remembered as “herniated disc in neck.” Lumbar disc herniation, meanwhile, refers to a protrusion in the lower spine.
Also, the spelling “disk” is correct, but “disc” is most common.
Symptoms of Disk Herniation
It is possible to have a herniated disk but experience no symptoms. Ruptured disks are sometimes only detected when X-rays are taken for other purposes. However, a ruptured disk can also be very painful or cause numbness or weakness.
First, pain and numbness can result from nerves being affected directly by the hernia. Second, weaknesses can result when the muscles associated with those nerves are affected. This weakness might be seen in a person stumbling or being unable to hold or lift items as they normally would.
The location of pain, numbness or weakness varies with the location of the slipped disk on the spine; different discs affect different nerves and associated muscles. Most slipped disks occur in the lower back or lumbar region of the spine. These types of herniated disk can affect the buttocks, legs and feet. In contrast, if a cervical (neck) disk ruptures, it might be sensed in the shoulders and/or arms.
Herniated disc symptoms might be especially intense when a person coughs, sneezes or moves the spine a certain way.
How is a Herniated Disc Diagnosed?
Lumbar or cervical disc herniation is rarely caused by a single event. Rather, it results from gradual degeneration. Part of this degeneration can be expected with aging; spinal discs naturally lose some of their moisture content and flexibility as a person becomes older. People sometimes exacerbate natural wear and tear by using their back muscles instead of their leg muscles to lift heavy objects.
People who sense sharp pain up and down the back of legs and back are commonly diagnosed with a herniated disc, particularly if the pain is chronic. Other signs of ruptured or leaking discs include soreness in particular spot.
Herniated Disc Treatment
Herniated disc treatment can be very conservative and low-cost. In most cases, a person need only perform exercises, use ice or heat therapy, and avoid putting their spine in certain positions. Slipped disc symptoms might then disappear within one or two months.
In some cases, disc herniation patients are advised to take heavy over-the-counter pain medications containing acetaminophen, ibuprofen or naproxen. A drawback to this is the potential for liver damage. Even stronger pain medication in the form of narcotics (e.g., hydrocodone) may be prescribed if the pain is intense. In addition to potentially causing liver damage, these drugs can cause confusion, sedation, nausea and constipation.
If symptoms of herniation do not subside with six weeks, a doctor might recommend cortisone injections. Cortisone injections suppress inflammation in the area surrounding spinal nerves.
A final option for treatment is surgery, but it is very rarely recommended. It is most often performed when slipped disc symptoms last more for six weeks, when a person has intense pain, or when a person is unable to walk. A herniated disc surgery is almost always necessary when a vertebra is fractured.
Herniated disc surgery usually requires removing only the protruding section of the disc. However, sometimes an entire intervertebral disc must be removed. It might be replaced with artificial cartilage. If no artificial disc is added, then the adjacent vertebrae will likely be fused together during surgery to keep the spine stable. As always speak with your doctor before embarking on any treatment methods independently and to make sure that the condition you are experiencing is indeed due to a herniated disk in the spine.